Kafka 服务启动、网络与线程模型
1 Kafka 服务启动流程
Kafka 服务启动流程代码,在 BrokerServer.scala 下的 startup() 方法中,该方法实例化了 LogManager、SocketServer 和 KafkaRequestHandlers 三个关键组件,代码如下。
/**
* Start up API for bringing up a single instance of the Kafka server.
* Instantiates the LogManager, the SocketServer and the request handlers - KafkaRequestHandlers
*/
override def startup(): Unit = {
// ...
try {
sharedServer.startForBroker()
info("Starting broker")
// ...
// 启动 KafkaScheduler,定时任务会通过此类中的线程池执行。
/* start scheduler */
kafkaScheduler = new KafkaScheduler(config.backgroundThreads)
kafkaScheduler.startup()
// 初始化 Broker 各种指标信息。
/* register broker metrics */
brokerTopicStats = new BrokerTopicStats(java.util.Optional.of(config))
// ...
// 初始化 MetadataCache。
metadataCache = MetadataCache.kRaftMetadataCache(config.nodeId)
// 启动 LogManager
// 负责日志的创建、检索、清理。
// Create log manager, but don't start it because we need to delay any potential unclean shutdown log recovery
// until we catch up on the metadata log and have up-to-date topic and broker configs.
logManager = LogManager(config, initialOfflineDirs, metadataCache, kafkaScheduler, time,
brokerTopicStats, logDirFailureChannel, keepPartitionMetadataFile = true)
// ...
// 创建 SocketServer 并启动 Acceptor 线程。
// Create and start the socket server acceptor threads so that the bound port is known.
// Delay starting processors until the end of the initialization sequence to ensure
// that credentials have been loaded before processing authentications.
socketServer = new SocketServer(config, metrics, time, credentialProvider, apiVersionManager)
// 初始化 ClientQuotaMetadataManager,管理配额。
clientQuotaMetadataManager = new ClientQuotaMetadataManager(quotaManagers, socketServer.connectionQuotas)
// ...
// 在 Kraft 模式下是 DefaultAlterPartitionManager 对象,
// 通过向 Controller 发送 AlertPartition 请求,更新 ISR 信息。
alterPartitionManager = AlterPartitionManager(
config,
metadataCache,
scheduler = kafkaScheduler,
controllerNodeProvider,
time = time,
metrics,
s"broker-${config.nodeId}-",
brokerEpochSupplier = () => lifecycleManager.brokerEpoch
)
alterPartitionManager.start()
// ...
// 创建 ReplicaManager 管理副本信息。
this._replicaManager = new ReplicaManager(
config = config,
metrics = metrics,
time = time,
scheduler = kafkaScheduler,
logManager = logManager,
remoteLogManager = remoteLogManagerOpt,
quotaManagers = quotaManagers,
metadataCache = metadataCache,
logDirFailureChannel = logDirFailureChannel,
alterPartitionManager = alterPartitionManager,
brokerTopicStats = brokerTopicStats,
isShuttingDown = isShuttingDown,
zkClient = None,
threadNamePrefix = None, // The ReplicaManager only runs on the broker, and already includes the ID in thread names.
delayedRemoteFetchPurgatoryParam = None,
brokerEpochSupplier = () => lifecycleManager.brokerEpoch,
addPartitionsToTxnManager = Some(addPartitionsToTxnManager)
)
// ...
// 创建 GroupCoordinator
// 管理和协调属于同一个消费者组的多个消费者实例
groupCoordinator = createGroupCoordinator()
// ...
// 创建 TransactionCoordinator。
// Create transaction coordinator, but don't start it until we've started replica manager.
// Hardcode Time.SYSTEM for now as some Streams tests fail otherwise, it would be good to fix the underlying issue
transactionCoordinator = TransactionCoordinator(config, replicaManager,
new KafkaScheduler(1, true, "transaction-log-manager-"),
producerIdManagerSupplier, metrics, metadataCache, Time.SYSTEM)
// ...
// 启动 BrokerLifecycleManager 管理 Broker 状态。
// 其中 BrokerToControllerChannelManager 的作用是:管理 Broker 到 Controller 的连接。
val brokerLifecycleChannelManager = BrokerToControllerChannelManager(
controllerNodeProvider,
time,
metrics,
config,
"heartbeat",
s"broker-${config.nodeId}-",
config.brokerSessionTimeoutMs / 2 // KAFKA-14392
)
lifecycleManager.start(
() => sharedServer.loader.lastAppliedOffset(),
brokerLifecycleChannelManager,
sharedServer.metaProps.clusterId,
networkListeners,
featuresRemapped
)
// ...
// 创建处理请求的 Processor 对象 (KafkaApis)。
// Create the request processor objects.
val raftSupport = RaftSupport(forwardingManager, metadataCache)
dataPlaneRequestProcessor = new KafkaApis(
requestChannel = socketServer.dataPlaneRequestChannel,
metadataSupport = raftSupport,
replicaManager = replicaManager,
groupCoordinator = groupCoordinator,
txnCoordinator = transactionCoordinator,
autoTopicCreationManager = autoTopicCreationManager,
brokerId = config.nodeId,
config = config,
configRepository = metadataCache,
metadataCache = metadataCache,
metrics = metrics,
authorizer = authorizer,
quotas = quotaManagers,
fetchManager = fetchManager,
brokerTopicStats = brokerTopicStats,
clusterId = clusterId,
time = time,
tokenManager = tokenManager,
apiVersionManager = apiVersionManager)
// 创建 KafkaRequestHandlerPool, Processor 线程个数通过配置文件 num.io.threads 配置
dataPlaneRequestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.nodeId,
socketServer.dataPlaneRequestChannel, dataPlaneRequestProcessor, time,
config.numIoThreads, s"${DataPlaneAcceptor.MetricPrefix}RequestHandlerAvgIdlePercent",
DataPlaneAcceptor.ThreadPrefix)
// ...
maybeChangeStatus(STARTING, STARTED)
}
catch {
case e: Throwable =>
maybeChangeStatus(STARTING, STARTED)
fatal("Fatal error during broker startup. Prepare to shutdown", e)
shutdown()
throw if (e.isInstanceOf[ExecutionException]) e.getCause else e
}
}2 Kafka 网络 IO 线程模型
Kafka 服务启动时创建并启动了 SocketServer 对象。Kafka 网络 IO 线程模型相关代码封装在 SocketServer.scala 中。
官方对 SocketServer 的介绍如下。
Handles new connections, requests and responses to and from broker. Kafka supports two types of request planes :
- data-plane :
- Handles requests from clients and other brokers in the cluster.
- The threading model is 1 Acceptor thread per listener, that handles new connections. It is possible to configure multiple data-planes by specifying multiple “,” separated endpoints for “listeners” in KafkaConfig. Acceptor has N Processor threads that each have their own selector and read requests from sockets M Handler threads that handle requests and produce responses back to the processor threads for writing.
- control-plane :
- Handles requests from controller. This is optional and can be configured by specifying “control. plane. listener. name”. If not configured, the controller requests are handled by the data-plane.
- The threading model is 1 Acceptor thread that handles new connections Acceptor has 1 Processor thread that has its own selector and read requests from the socket. 1 Handler thread that handles requests and produces responses back to the processor thread for writing.
由简介可知 SocketServer 的功能是处理新连接、接受并响应请求。分为数据平面和控制平面,我们本节主要看数据平面的线程模型。
在创建 SocketServer 时,调用 createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors() 方法,创建数据平面的 Acceptor 和 Processor。
// data-plane
private[network] val dataPlaneAcceptors = new ConcurrentHashMap[EndPoint, DataPlaneAcceptor]()
// 创建 RequestChannel 对象,内部封装了
// requestQueue: 阻塞队列,
// processors: 执行线程
// callbackQueue:
val dataPlaneRequestChannel = new RequestChannel(maxQueuedRequests, DataPlaneAcceptor.MetricPrefix, time, apiVersionManager.newRequestMetrics)
// ...
// 调用 createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors 方法。
// Create acceptors and processors for the statically configured endpoints when the
// SocketServer is constructed. Note that this just opens the ports and creates the data
// structures. It does not start the acceptors and processors or their associated JVM
// threads.
config.dataPlaneListeners.foreach(createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors)
// ...
def createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors(endpoint: EndPoint): Unit = synchronized {
// ...
// 创建 Acceptor,为该 Acceptor 绑定 dataPlaneRequestChannel。
val dataPlaneAcceptor = createDataPlaneAcceptor(endpoint, isPrivilegedListener, dataPlaneRequestChannel)
// ...
dataPlaneAcceptors.put(endpoint, dataPlaneAcceptor)
info(s"Created data-plane acceptor and processors for endpoint : ${endpoint.listenerName}")
}2.1 Acceptor 的创建与工作流程
Acceptor 实现了 Runnable 接口,封装了一个 Selector: nioSelector 和一个执行线程: thread。
BrokerServer 通过调用 socketServer.enableRequestProcessing 方法,启动 Acceptor 和 Processors 线程。
Acceptor 的重要属性和方法如下。
/**
* Thread that accepts and configures new connections. There is one of these per endpoint.
*/
private[kafka] abstract class Acceptor(...)
extends Runnable with Logging {
// ...
// Java 中的 Selector
private val nioSelector = NSelector.open()
// Java NIO 中,ServerSocketChannel 是可以监听新来的 TCP 连接的通道,就像标准 I/O 中的 ServerSocket 一样。它的主要作用是监听新的连接请求,当一个新的连接建立时,会创建一个新的 SocketChannel 来代表这个连接。
private[network] var serverChannel: ServerSocketChannel = _
// Processors 线程
private[network] val processors = new ArrayBuffer[Processor]()
val thread = KafkaThread.nonDaemon(
s"${threadPrefix()}-kafka-socket-acceptor-${endPoint.listenerName}-${endPoint.securityProtocol}-${endPoint.port}",
this)
// socketServer.enableRequestProcessing 方法会调用 start() 方法,从而调用 thread.start()。
def start(): Unit = synchronized {
try {
// ...
// 创建 ServerSocketChannel 用于监听连接建立请求
if (serverChannel == null) {
serverChannel = openServerSocket(endPoint.host, endPoint.port, listenBacklogSize)
debug(s"Opened endpoint ${endPoint.host}:${endPoint.port}")
}
// 启动 Processors 线程
debug(s"Starting processors for listener ${endPoint.listenerName}")
processors.foreach(_.start())
// 启动 Acceptor 线程,调用 Acceptor::run() 方法
debug(s"Starting acceptor thread for listener ${endPoint.listenerName}")
thread.start()
startedFuture.complete(null)
started = true
} catch {
case e: ClosedChannelException =>
debug(s"Refusing to start acceptor for ${endPoint.listenerName} since the acceptor has already been shut down.")
startedFuture.completeExceptionally(e)
case t: Throwable =>
error(s"Unable to start acceptor for ${endPoint.listenerName}", t)
startedFuture.completeExceptionally(new RuntimeException(s"Unable to start acceptor for ${endPoint.listenerName}", t))
}
}
// ...
/**
* Accept loop that checks for new connection attempts
*/
override def run(): Unit = {
// nioSelector 注册 OP_ACCEPT 事件
serverChannel.register(nioSelector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)
try {
while (shouldRun.get()) {
try {
// 接受新的连接请求
acceptNewConnections()
closeThrottledConnections()
}
catch {
// We catch all the throwables to prevent the acceptor thread from exiting on exceptions due
// to a select operation on a specific channel or a bad request. We don't want
// the broker to stop responding to requests from other clients in these scenarios.
case e: ControlThrowable => throw e
case e: Throwable => error("Error occurred", e)
}
}
} finally {
debug("Closing server socket, selector, and any throttled sockets.")
CoreUtils.swallow(serverChannel.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
CoreUtils.swallow(nioSelector.close(), this, Level.ERROR)
throttledSockets.foreach(throttledSocket => closeSocket(throttledSocket.socket, this))
throttledSockets.clear()
}
}
}在 start() 方法中,调用 openServerSocket() 方法创建并启动一个 ServerSocketChannel 对象。
openServerSocket() 方法通过调用 ServerSocketChannel.open() 方法创建并启动 ServerSocketChannel 对象,代码如下。
/**
* Create a server socket to listen for connections on.
*/
private def openServerSocket(host: String, port: Int, listenBacklogSize: Int): ServerSocketChannel = {
val socketAddress =
if (Utils.isBlank(host))
new InetSocketAddress(port)
else
new InetSocketAddress(host, port)
// 创建 ServerSocketChannel,监听新连接
val serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open()
// 设置 Blocking 模式为 false
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false)
// 设置 ServerSocket 的 SO_RCVBUF
if (recvBufferSize != Selectable.USE_DEFAULT_BUFFER_SIZE)
// The value of SO_RCVBUF is used both to set the size of the internal socket receive buffer, and to set the size of the TCP receive window that is advertised to the remote peer.
serverChannel.socket().setReceiveBufferSize(recvBufferSize)
try {
// 绑定 IP:Port 并指定 backlog 大小
// backlog 参数的意思:The backlog argument is the requested maximum number of pending connections on the socket.
serverChannel.socket.bind(socketAddress, listenBacklogSize)
info(s"Awaiting socket connections on ${socketAddress.getHostString}:${serverChannel.socket。getLocalPort}.")
} catch {
case e: SocketException =>
throw new KafkaException(s"Socket server failed to bind to ${socketAddress.getHostString}:$port: ${e.getMessage}.", e)
}
serverChannel
}在 run() 方法中,先为 nioSelector 注册 OP_ACCEPT 事件,再循环调用 acceptNewConnections() 方法将监听到的新连接分配给 Processors 线程处理。
acceptNewConnections() 方法代码如下。
/**
* Listen for new connections and assign accepted connections to processors using round-robin.
*/
private def acceptNewConnections(): Unit = {
// Selects a set of keys whose corresponding channels are ready for I/O operations.
val ready = nioSelector.select(500)
if (ready > 0) {
// Returns this selector's selected-key set.
val keys = nioSelector.selectedKeys()
val iter = keys.iterator()
while (iter.hasNext && shouldRun.get()) {
try {
val key = iter.next
iter.remove()
if (key.isAcceptable) {
// accept 方法,Accept 一个新连接,返回 SocketChannel
accept(key).foreach { socketChannel =>
// Assign the channel to the next processor (using round-robin) to which the
// channel can be added without blocking. If newConnections queue is full on
// all processors, block until the last one is able to accept a connection.
var retriesLeft = synchronized(processors.length)
// 使用 round-robin 为 socketChannel 分配 Processor
var processor: Processor = null
do {
retriesLeft -= 1
processor = synchronized {
// adjust the index (if necessary) and retrieve the processor atomically for
// correct behaviour in case the number of processors is reduced dynamically
currentProcessorIndex = currentProcessorIndex % processors.length
processors(currentProcessorIndex)
}
currentProcessorIndex += 1
} while (!assignNewConnection(socketChannel, processor, retriesLeft == 0))
}
} else
throw new IllegalStateException("Unrecognized key state for acceptor thread.")
} catch {
case e: Throwable => error("Error while accepting connection", e)
}
}
}
}
/**
* Accept a new connection
*/
private def accept(key: SelectionKey): Option[SocketChannel] = {
val serverSocketChannel = key.channel().asInstanceOf[ServerSocketChannel]
// Accepts a connection made to this channel's socket.
val socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept()
try {
connectionQuotas.inc(endPoint.listenerName, socketChannel.socket.getInetAddress, blockedPercentMeter)
// 配置 SocketChannel
// 1. Block = false
// 2. TCP_NODELAY = true
// 3. SO_KEEPALIVE = true
configureAcceptedSocketChannel(socketChannel)
Some(socketChannel)
} catch {
case e: TooManyConnectionsException =>
info(s"Rejected connection from ${e.ip}, address already has the configured maximum of ${e.count} connections.")
connectionQuotas.closeChannel(this, endPoint.listenerName, socketChannel)
None
case e: ConnectionThrottledException =>
val ip = socketChannel.socket.getInetAddress
debug(s"Delaying closing of connection from $ip for ${e.throttleTimeMs} ms")
val endThrottleTimeMs = e.startThrottleTimeMs + e.throttleTimeMs
throttledSockets += DelayedCloseSocket(socketChannel, endThrottleTimeMs)
None
case e: IOException =>
error(s"Encountered an error while configuring the connection, closing it.", e)
connectionQuotas.closeChannel(this, endPoint.listenerName, socketChannel)
None
}
}acceptNewConnections() 方法调用 assignNewConnection() 将 SocketChannel 加入到 Processor 的阻塞队列 newConnections 中,然后调用 wakeup() 方法唤醒 Processor 中的 selector。
assignNewConnection() 方法代码如下。
private def assignNewConnection(socketChannel: SocketChannel, processor: Processor, mayBlock: Boolean): Boolean = {
// 调用 Processor 的 accept 方法
processor.accept(socketChannel, mayBlock, blockedPercentMeter)
}
/**
* Queue up a new connection for reading
*/
def accept(socketChannel: SocketChannel,
mayBlock: Boolean,
acceptorIdlePercentMeter: com.yammer.metrics.core.Meter): Boolean = {
val accepted = {
// 将 socketChannel 加入到 newConnections 阻塞队列中
if (newConnections.offer(socketChannel))
true
else if (mayBlock) {
val startNs = time.nanoseconds
newConnections.put(socketChannel)
acceptorIdlePercentMeter.mark(time.nanoseconds() - startNs)
true
} else
false
}
if (accepted)
// Wakeup the thread for selection.
// Interrupt the nioSelector if it is blocked waiting to do I/O.
// def wakeup(): Unit = selector.wakeup()
wakeup()
accepted
}至此,我们使用 Acceptor 创建了一个 ServerSocketChannel 并使用 nioSelector 监听 OP_ACCEPT 事件,将新连接加入到 Processor 的阻塞队列 newConnections 中,最后把新连接交给 Processor 处理。
2.2 Processor 的创建与工作流程
SocketServer 的 createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors() 方法,在创建完 Acceptor 后会创建 Processor。代码如下所示。
def createDataPlaneAcceptorAndProcessors(endpoint: EndPoint): Unit = synchronized {
// ...
// 创建 Acceptor
val dataPlaneAcceptor = createDataPlaneAcceptor(endpoint, isPrivilegedListener, dataPlaneRequestChannel)
// ...
// 通过配置创建 Processor
dataPlaneAcceptor.configure(parsedConfigs)
// ...
}
/**
* Configure this class with the given key-value pairs
*/
override def configure(configs: util.Map[String, _]): Unit = {
// 调用 addProcessors 创建 Processor。Processor 个数为 num.network.threads 。
addProcessors(configs.get(KafkaConfig.NumNetworkThreadsProp).asInstanceOf[Int])
}
def addProcessors(toCreate: Int): Unit = synchronized {
val listenerName = endPoint.listenerName
val securityProtocol = endPoint.securityProtocol
val listenerProcessors = new ArrayBuffer[Processor]()
for (_ <- 0 until toCreate) {
// 创建 Processor 线程
val processor = newProcessor(socketServer.nextProcessorId(), listenerName, securityProtocol)
listenerProcessors += processor
// 在 Acceptor 对应的 requestChannel 下,存放 Processor 引用
requestChannel.addProcessor(processor)
if (started) {
processor.start()
}
}
// 加入到 Acceptor.processors 中
processors ++= listenerProcessors
}Processor 的重要属性和方法如下。
/**
* Thread that processes all requests from a single connection. There are N of these running in parallel
* each of which has its own selector
*/
private[kafka] class Processor()
extends Runnable with Logging {
// Processor 线程
val thread = KafkaThread.nonDaemon(threadName, this)
// 存放 Acceptor 分发的新连接
private val newConnections = new ArrayBlockingQueue[SocketChannel](connectionQueueSize)
private val inflightResponses = mutable.Map[String, RequestChannel.Response]()
private val responseQueue = new LinkedBlockingDeque[RequestChannel.Response]()
// Processor 的 selector
private[network] val selector = createSelector(
ChannelBuilders.serverChannelBuilder(
listenerName,
listenerName == config.interBrokerListenerName,
securityProtocol,
config,
credentialProvider.credentialCache,
credentialProvider.tokenCache,
time,
logContext,
() => apiVersionManager.apiVersionResponse(throttleTimeMs = 0)
)
)
}在调用 Acceptor.start() 方法时会启动 Processor 线程。Processor 的 run() 方法如下所示。
override def run(): Unit = {
try {
while (shouldRun.get()) {
try {
// 配置 newConnections 中的新连接,注册 OP_READ 事件
// setup any new connections that have been queued up
configureNewConnections()
// 将 responseQueue 中的连接,注册 OP_WRITE 事件,并设置响应内容
// register any new responses for writing
processNewResponses()
// 执行 selector 注册的所有类型 I/O
poll()
// 将接收的请求放入 RequestChannel.requestQueue 中
// KafkaRequestHandler 会从 RequestChannel.requestQueue 中获取请求并处理
processCompletedReceives()
// 执行响应的回调函数
processCompletedSends()
processDisconnected()
closeExcessConnections()
} catch {
case e: Throwable => processException("Processor got uncaught exception.", e)
}
}
} finally {
debug(s"Closing selector - processor $id")
CoreUtils.swallow(closeAll(), this, Level.ERROR)
}
}Processor 先注册 OP_READ 和 OP_WRITE 事件,调用 poll() 方法执行 I/O 操作,再通过 processCompletedReceives() 方法,将接收的请求放入 RequestChannel.requestQueue 队列中。
3 I/O 多路复用
I/O Multiplexing: The select and poll Functions
4 执行线程模型
在 Kafka 服务启动时,会创建请求处理线程池 dataPlaneRequestHandlerPool 。代码如下。
override def startup(): Unit = {
dataPlaneRequestHandlerPool = new KafkaRequestHandlerPool(config.nodeId,
socketServer.dataPlaneRequestChannel, dataPlaneRequestProcessor, time,
config.numIoThreads, s"${DataPlaneAcceptor.MetricPrefix}RequestHandlerAvgIdlePercent",
DataPlaneAcceptor.ThreadPrefix)
}创建 KafkaRequestHandlerPool 时会创建 KafkaRequestHandler 线程,并启动这些线程。代码如下。
class KafkaRequestHandlerPool(val brokerId: Int,
val requestChannel: RequestChannel,
val apis: ApiRequestHandler,
time: Time,
numThreads: Int,
requestHandlerAvgIdleMetricName: String,
logAndThreadNamePrefix : String) extends Logging {
// 线程池大小
private val threadPoolSize: AtomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(numThreads)
// 线程池数组
val runnables = new mutable.ArrayBuffer[KafkaRequestHandler](numThreads)
for (i <- 0 until numThreads) {
createHandler(i)
}
// 创建线程并在后台执行
def createHandler(id: Int): Unit = synchronized {
runnables += new KafkaRequestHandler(id, brokerId, aggregateIdleMeter, threadPoolSize, requestChannel, apis, time)
KafkaThread.daemon(logAndThreadNamePrefix + "-kafka-request-handler-" + id, runnables(id)).start()
}
}KafkaRequestHandler 的 run() 方法,会调用 KafkaApis.handle() 方法执行请求。代码如下。
/**
* A thread that answers kafka requests.
*/
class KafkaRequestHandler(id: Int,
brokerId: Int,
val aggregateIdleMeter: Meter,
val totalHandlerThreads: AtomicInteger,
val requestChannel: RequestChannel,
apis: ApiRequestHandler,
time: Time) extends Runnable with Logging {
def run(): Unit = {
threadRequestChannel.set(requestChannel)
while (!stopped) {
// requestQueue.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
// 从 RequestChannel.requestQueue 获取请求
val req = requestChannel.receiveRequest(300)
req match {
case RequestChannel.ShutdownRequest =>
debug(s"Kafka request handler $id on broker $brokerId received shut down command")
completeShutdown()
return
case callback: RequestChannel.CallbackRequest =>
// ...
case request: RequestChannel.Request =>
try {
request.requestDequeueTimeNanos = endTime
trace(s"Kafka request handler $id on broker $brokerId handling request $request")
threadCurrentRequest.set(request)
// 调用 apis.handle,交给 KafkaApis 处理请求
apis.handle(request, requestLocal)
} catch {
case e: FatalExitError =>
completeShutdown()
Exit.exit(e.statusCode)
case e: Throwable => error("Exception when handling request", e)
} finally {
threadCurrentRequest.remove()
request.releaseBuffer()
}
case RequestChannel.WakeupRequest =>
// We should handle this in receiveRequest by polling callbackQueue.
warn("Received a wakeup request outside of typical usage.")
case null => // continue
}
}
completeShutdown()
}
}KafkaApis.handle() 方法,负责分发并处理请求。代码如下。
override def handle(request: RequestChannel.Request, requestLocal: RequestLocal): Unit = {
// 分发并处理请求
request.header.apiKey match {
case ApiKeys.PRODUCE => handleProduceRequest(request, requestLocal)
case ApiKeys.FETCH => handleFetchRequest(request)
case ApiKeys.LIST_OFFSETS => handleListOffsetRequest(request)
// ...
}
}5 Kafka 网络和线程模型总结
最后用一张流程图总结 Kafka 网络 IO 模型和线程模型。
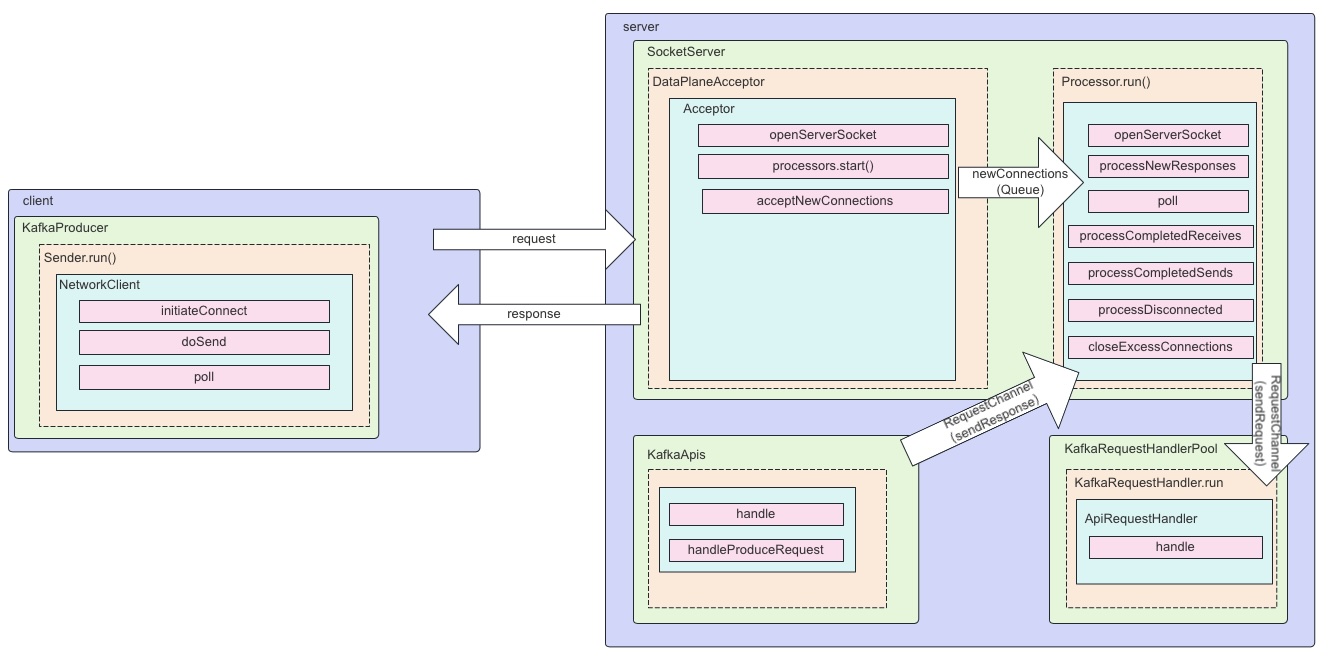
How Kafka Works: Understand Kafka Network Communication and Thread Model