Redis 紧凑列表 (listpack)
1 紧凑列表的结构
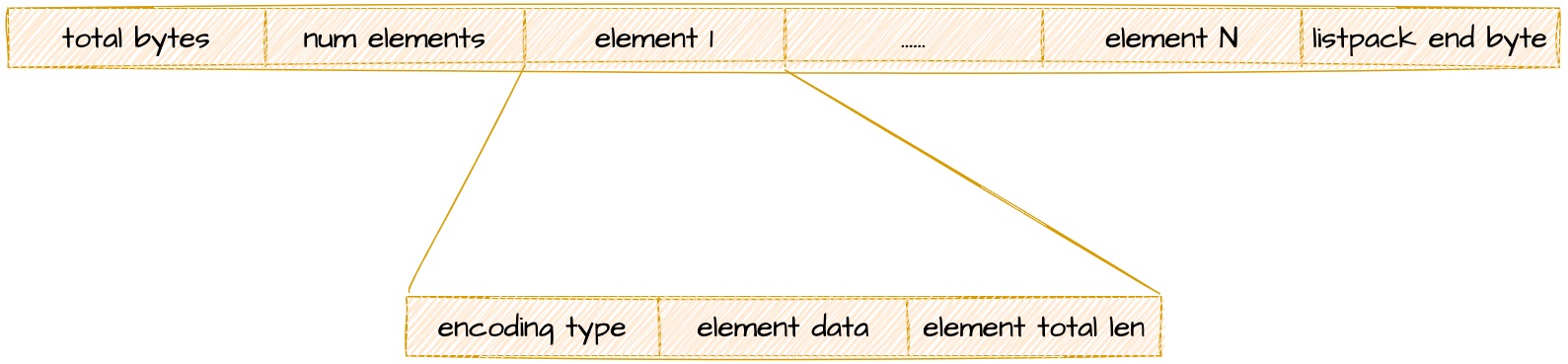
紧凑列表更加详细的结构,可以参考 listpack 规格设计。
1.1 紧凑列表元数据
- total bytes: 32 bit 无符号整数,存储 listpack 的字节大小;
- num elements: 16 bit 无符号整数,存储 listpack 结点个数;
- listpack end byte: 一个字节,值为 0xFF。
1.1.1 紧凑列表元数据的宏定义
-
LP_HDR_SIZE: 表示一个 listpack header 部分的字节大小;
-
LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN: 因为 listpack 里记录结点数量只用了两个字节存储,最大能记录 65535 个结点。当结点个数超过了这个限制,就会将 num elements 设置为 LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN,表示结点数量未知,真实的结点数量需要遍历 listpack 才能获取到。
-
lpGetTotalBytes: 从 listpack 的前四个字节里,获取 listpack 占用的字节数,时间复杂度 O(1);
-
lpGetNumElements:从 listpack 的第五个和第六个字节里,获取 listpack 的结点数量,时间复杂度O(1) ;
-
lpSetTotalBytes:设置 listpack 占用的字节数;
-
lpSetNumElements:设置 listpack 的结点数量。
#define LP_HDR_SIZE 6 /* 32 bit total len + 16 bit number of elements. */
#define LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN UINT16_MAX
#define LP_EOF 0xFF
#define lpGetTotalBytes(p) (((uint32_t)(p)[0]<<0) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[1]<<8) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[2]<<16) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[3]<<24))
#define lpGetNumElements(p) (((uint32_t)(p)[4]<<0) | \
((uint32_t)(p)[5]<<8))
#define lpSetTotalBytes(p,v) do { \
(p)[0] = (v)&0xff; \
(p)[1] = ((v)>>8)&0xff; \
(p)[2] = ((v)>>16)&0xff; \
(p)[3] = ((v)>>24)&0xff; \
} while(0)
#define lpSetNumElements(p,v) do { \
(p)[4] = (v)&0xff; \
(p)[5] = ((v)>>8)&0xff; \
} while(0)1.2 紧凑列表结点
- encoding type: 结点数据对应的编码方式,包含编码类型、数据字节数等信息;
- element data: 结点实际数据内容;
- element total len: 记录 encoding type 和 element data 占用的字节总数,不包含自身长度,反向遍历中使用。
1.3 紧凑列表结点结构体
每个紧凑列表存储的都是一个字符串或者整数:
- 当存储字符串时,sval 存储字符串数据,slen 存储字符串长度;
- 当存储整数时,lval 存储整数数据,sval 为 NULL。
/* Each entry in the listpack is either a string or an integer. */
typedef struct {
/* When string is used, it is provided with the length (slen). */
unsigned char *sval;
uint32_t slen;
/* When integer is used, 'sval' is NULL, and lval holds the value. */
long long lval;
} listpackEntry;2 紧凑列表 API
2.1 lpNew
lpNew 创建一个空的 listpack,capacity 为申请的字节数。
/* Create a new, empty listpack.
* On success the new listpack is returned, otherwise an error is returned.
* Pre-allocate at least `capacity` bytes of memory,
* over-allocated memory can be shrunk by `lpShrinkToFit`.
* */
unsigned char *lpNew(size_t capacity) {
// 一个空的 listpack 最少需要分配 LP_HDR_SIZE+1 字节, 即 LP_HDR_SIZE + LP_EOF
unsigned char *lp = lp_malloc(capacity > LP_HDR_SIZE+1 ? capacity : LP_HDR_SIZE+1);
if (lp == NULL) return NULL;
// 设置空 listpack 的字节大小
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,LP_HDR_SIZE+1);
// 设置结点个数
lpSetNumElements(lp,0);
// 为 EOF 赋值
lp[LP_HDR_SIZE] = LP_EOF;
return lp;
}2.2 lpSkip
lpSkip 跳过当前结点,返回下一个结点。
/* Skip the current entry returning the next. It is invalid to call this
* function if the current element is the EOF element at the end of the
* listpack, however, while this function is used to implement lpNext(),
* it does not return NULL when the EOF element is encountered. */
unsigned char *lpSkip(unsigned char *p) {
// 获取结点大小,不包括 backlen
unsigned long entrylen = lpCurrentEncodedSizeUnsafe(p);
// 获取当前结点的 backlen 大小,合起来为当前结点实际占用字节数
entrylen += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,entrylen);
// 跳过当前结点
p += entrylen;
return p;
}2.3 lpNext
lpNext 返回后继结点,如果已经是 listpack 的末尾,返回 NULL。
/* If 'p' points to an element of the listpack, calling lpNext() will return
* the pointer to the next element (the one on the right), or NULL if 'p'
* already pointed to the last element of the listpack. */
unsigned char *lpNext(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p) {
assert(p);
p = lpSkip(p);
if (p[0] == LP_EOF) return NULL;
lpAssertValidEntry(lp, lpBytes(lp), p);
return p;
}2.4 lpPrev
lpPrev 返回前驱结点,如果已经是 listpack 的首结点,返回 NULL。
/* If 'p' points to an element of the listpack, calling lpPrev() will return
* the pointer to the previous element (the one on the left), or NULL if 'p'
* already pointed to the first element of the listpack. */
unsigned char *lpPrev(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *p) {
assert(p);
// 现在 p 指向的是 listpack 的第一个结点,返回 NULL
if (p-lp == LP_HDR_SIZE) return NULL;
// 指向前一个结点的 backlen
p--; /* Seek the first backlen byte of the last element. */
// 解析 backlen 的值,获取 encoding + content 字节数
uint64_t prevlen = lpDecodeBacklen(p);
// 获得前驱结点总占用字节数
prevlen += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,prevlen);
// p 指针向前偏移 prevlen-1 个字节,指向前驱结点(之前已经向前偏移了一个字节)
p -= prevlen-1; /* Seek the first byte of the previous entry. */
lpAssertValidEntry(lp, lpBytes(lp), p);
return p;
}2.5 lpLength
lpLength 获取结点数量。如果元素个数为 LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN,会遍历整个 listpack 获取长度。
/* Return the number of elements inside the listpack. This function attempts
* to use the cached value when within range, otherwise a full scan is
* needed. As a side effect of calling this function, the listpack header
* could be modified, because if the count is found to be already within
* the 'numele' header field range, the new value is set. */
unsigned long lpLength(unsigned char *lp) {
uint32_t numele = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (numele != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) return numele;
/* Too many elements inside the listpack. We need to scan in order
* to get the total number. */
uint32_t count = 0;
unsigned char *p = lpFirst(lp);
while(p) {
count++;
p = lpNext(lp,p);
}
/* If the count is again within range of the header numele field,
* set it. */
if (count < LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) lpSetNumElements(lp,count);
return count;
}2.6 lpInsert
lpInsert 向 listpack 中插入一个结点。
这是一个核心函数,lpPrepend、lpAppend、lpReplace、lpDelete 都是调用 lpInsert 函数,实现向前插入一个结点、向后插入一个结点、替换结点、用空替换结点(删除)等功能。
/* Insert, delete or replace the specified string element 'elestr' of length
* 'size' or integer element 'eleint' at the specified position 'p', with 'p'
* being a listpack element pointer obtained with lpFirst(), lpLast(), lpNext(),
* lpPrev() or lpSeek().
*
* The element is inserted before, after, or replaces the element pointed
* by 'p' depending on the 'where' argument, that can be LP_BEFORE, LP_AFTER
* or LP_REPLACE.
*
* If both 'elestr' and `eleint` are NULL, the function removes the element
* pointed by 'p' instead of inserting one.
* If `eleint` is non-NULL, 'size' is the length of 'eleint', the function insert
* or replace with a 64 bit integer, which is stored in the 'eleint' buffer.
* If 'elestr` is non-NULL, 'size' is the length of 'elestr', the function insert
* or replace with a string, which is stored in the 'elestr' buffer.
*
* Returns NULL on out of memory or when the listpack total length would exceed
* the max allowed size of 2^32-1, otherwise the new pointer to the listpack
* holding the new element is returned (and the old pointer passed is no longer
* considered valid)
*
* If 'newp' is not NULL, at the end of a successful call '*newp' will be set
* to the address of the element just added, so that it will be possible to
* continue an interaction with lpNext() and lpPrev().
*
* For deletion operations (both 'elestr' and 'eleint' set to NULL) 'newp' is
* set to the next element, on the right of the deleted one, or to NULL if the
* deleted element was the last one. */
unsigned char *lpInsert(unsigned char *lp, unsigned char *elestr, unsigned char *eleint,
uint32_t size, unsigned char *p, int where, unsigned char **newp)
{
unsigned char intenc[LP_MAX_INT_ENCODING_LEN];
unsigned char backlen[LP_MAX_BACKLEN_SIZE];
uint64_t enclen; /* The length of the encoded element. */
// elestr 和 eleint 都为 NULL,则实际上是删除元素
int delete = (elestr == NULL && eleint == NULL);
/* when deletion, it is conceptually replacing the element with a
* zero-length element. So whatever we get passed as 'where', set
* it to LP_REPLACE. */
// 删除元素就是使用 NULL 替换元素,因此设置为 LP_REPLACE
if (delete) where = LP_REPLACE;
/* If we need to insert after the current element, we just jump to the
* next element (that could be the EOF one) and handle the case of
* inserting before. So the function will actually deal with just two
* cases: LP_BEFORE and LP_REPLACE. */
// 如果是 LP_AFTER 表示在当前结点后面插入元素,
// 则指向当前结点的后继结点,并将 where 替换为 LP_BEFORE
// 这样之后的代码只需要考虑 LP_BEFORE 和 LP_REPLACE 了。
if (where == LP_AFTER) {
p = lpSkip(p);
where = LP_BEFORE;
ASSERT_INTEGRITY(lp, p);
}
/* Store the offset of the element 'p', so that we can obtain its
* address again after a reallocation. */
// 记录下当前 p 在 lp 下的偏移量,这样在 listpack 内存重新分配后也能狗定位到 p
unsigned long poff = p-lp;
int enctype;
if (elestr) {
/* Calling lpEncodeGetType() results into the encoded version of the
* element to be stored into 'intenc' in case it is representable as
* an integer: in that case, the function returns LP_ENCODING_INT.
* Otherwise if LP_ENCODING_STR is returned, we'll have to call
* lpEncodeString() to actually write the encoded string on place later.
*
* Whatever the returned encoding is, 'enclen' is populated with the
* length of the encoded element. */
// lpEncodeGetType 对插入元素内容进行编码,返回编码类型
// 编码类型为 LP_ENCODING_INT 或者 LP_ENCODING_STR
// 对于 LP_ENCODING_INT 编码, encoding 会被写入到 intenc 变量中
// 无论是什么编码,都会将元素的长度 (encoding + content) 写入到 enclen 变量中
enctype = lpEncodeGetType(elestr,size,intenc,&enclen);
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) eleint = intenc;
} else if (eleint) {
enctype = LP_ENCODING_INT;
enclen = size; /* 'size' is the length of the encoded integer element. */
} else {
enctype = -1;
enclen = 0;
}
/* We need to also encode the backward-parsable length of the element
* and append it to the end: this allows to traverse the listpack from
* the end to the start. */
// 根据 enclen 编码 backlen,返回 backlen 的长度
unsigned long backlen_size = (!delete) ? lpEncodeBacklen(backlen,enclen) : 0;
// 获取当前 listpack 的总字节数
uint64_t old_listpack_bytes = lpGetTotalBytes(lp);
// 如果是 LP_REPLACE 操作,计算 replaced_len,否则该值为 0
uint32_t replaced_len = 0;
if (where == LP_REPLACE) {
replaced_len = lpCurrentEncodedSizeUnsafe(p);
replaced_len += lpEncodeBacklen(NULL,replaced_len);
ASSERT_INTEGRITY_LEN(lp, p, replaced_len);
}
// 计算新的 listpack 占用字节数
uint64_t new_listpack_bytes = old_listpack_bytes + enclen + backlen_size
- replaced_len;
if (new_listpack_bytes > UINT32_MAX) return NULL;
/* We now need to reallocate in order to make space or shrink the
* allocation (in case 'when' value is LP_REPLACE and the new element is
* smaller). However we do that before memmoving the memory to
* make room for the new element if the final allocation will get
* larger, or we do it after if the final allocation will get smaller. */
unsigned char *dst = lp + poff; /* May be updated after reallocation. */
/* Realloc before: we need more room. */
// 如果新的内存空间大于原本的看空间,需要为 listpack 申请新的内存空间
// dst 为新元素插入的位置
if (new_listpack_bytes > old_listpack_bytes &&
new_listpack_bytes > lp_malloc_size(lp)) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
/* Setup the listpack relocating the elements to make the exact room
* we need to store the new one. */
if (where == LP_BEFORE) {
// LP_BEFORE,将插入位置后面的结点后移,为新结点腾出空间
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,dst,old_listpack_bytes-poff);
} else { /* LP_REPLACE. */
// LP_REPLACE,调整被替换结点大小,后继结点向前或向后移动
memmove(dst+enclen+backlen_size,
dst+replaced_len,
old_listpack_bytes-poff-replaced_len);
}
/* Realloc after: we need to free space. */
// 释放多余空间
if (new_listpack_bytes < old_listpack_bytes) {
if ((lp = lp_realloc(lp,new_listpack_bytes)) == NULL) return NULL;
dst = lp + poff;
}
/* Store the entry. */
// listpack 的内存空间已经调整好,直接将元素插入到 dst 位置
if (newp) {
*newp = dst;
/* In case of deletion, set 'newp' to NULL if the next element is
* the EOF element. */
// 如果是删除元素,并且到达 listpack 末尾,则将 newp 赋值为 NULL
if (delete && dst[0] == LP_EOF) *newp = NULL;
}
if (!delete) {
if (enctype == LP_ENCODING_INT) {
// LP_ENCODING_INT,元素已经保存在 eleint 中,调用 memcpy 插入 listpack
memcpy(dst,eleint,enclen);
} else if (elestr) {
// LP_ENCODING_STRING 调用 lpEncodingString 保存元素内容
lpEncodeString(dst,elestr,size);
} else {
redis_unreachable();
}
// 偏移到结点末尾
dst += enclen;
// 写入 backlen
memcpy(dst,backlen,backlen_size);
// 偏移到下个结点
dst += backlen_size;
}
/* Update header. */
// 更新 listpack 中的 lpnumbers 和 lpbytes 属性
if (where != LP_REPLACE || delete) {
uint32_t num_elements = lpGetNumElements(lp);
if (num_elements != LP_HDR_NUMELE_UNKNOWN) {
if (!delete)
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements+1);
else
lpSetNumElements(lp,num_elements-1);
}
}
lpSetTotalBytes(lp,new_listpack_bytes);
return lp;
}